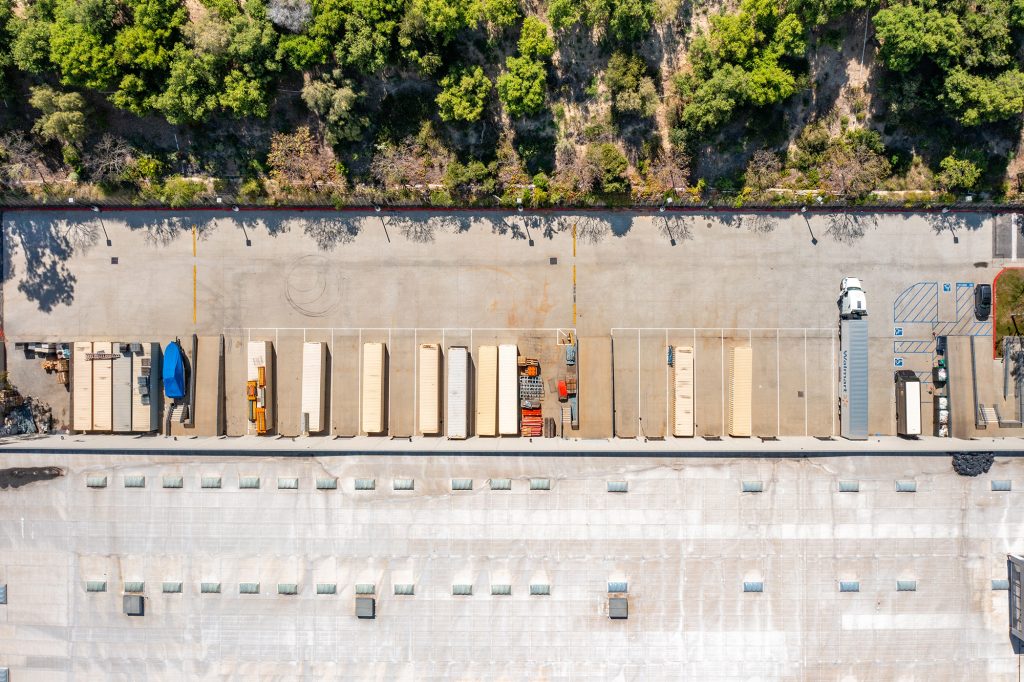
Shipping large orders requires coordination, compliance and cost management. Our freight logistics services provide end-to-end solutions for full truckload and less-than-truckload (LTL).
We manage carrier selection, routing, scheduling and documentation, giving brands visibility and control over their freight operations. Integrated tracking systems provide real-time updates, enabling precise coordination with fulfillment and inventory management.
Regardless of shipment type, our freight solutions reduce delays, optimize shipping costs and maintain the integrity of your products throughout transit. Scalable operations accommodate seasonal surges and expanding market reach without disrupting your supply chain.

Get your goods where they need to be precisely and quickly.
We handle everything from air freight to truckload shipments.
Simplifying logistics and supply chain management for every job.
At River Plate Inc., we redefine freight logistics with precision, innovation, and a relentless commitment to excellence. As a trusted freight broker and forwarder, we simplify transportation so that your cargo (whether via ocean freight or a partial truckload) reaches its destination with unmatched reliability. Our team collaborates with top carriers and shippers, ensuring that every shipment is managed efficiently from start to finish.
Need specialized services? No problem. We handle everything from customs brokerage and clearance to last-mile logistics so you don’t have to stress over red tape. Whether shipping across borders or managing domestic freight, we ensure your supply chain stays efficient, cost-effective, and always moving forward.
Our specialized services cater to your supply chain’s unique demands. Every step is optimized for timely delivery, ensuring your operations remain as efficient as they are dynamic.
What makes us stand out? Our services are designed to be as flexible as your business needs. Whether you’re looking for comprehensive ocean freight solutions or a tailored partial truckload strategy, our transportation experts are here to build a custom logistics plan. We handle the details—from booking with reliable carriers to managing the complexities of customs procedures—so you can concentrate on driving your business forward.
“Our company has been working with them for years now, and they’re wonderful to work with. Communicative and they always go the extra mile to make sure our orders go through fulfillment seamlessly.”
Erica Kim
Freight logistics is more than just moving goods from point A to point B—it’s about precision, reliability, and efficiency. At River Plate Inc., we’ve developed a seamless process that keeps your supply chain operations running smoothly, meeting demand while reducing delays and unnecessary costs. With a strong network of trucking companies, carriers, and industry experts, we ensure every shipment is handled carefully from pickup to final destination.
Strategic Planning and Coordination
Every incredible journey starts with a solid plan. We begin by analyzing current demand and mapping out the most efficient route for your shipment. Working closely with a network of trusted brokers and reputable trucking companies, we lay the groundwork for a smooth transit. Our expert team prepares each cargo unit precisely, setting it up for success.
In-Transit Management and Execution
Once your shipment is on the move, our focus shifts to meticulous in-transit management. We continuously monitor your freight, ensuring it stays on schedule. We carefully handle each detail, whether a full load or a partial truckload. Our dedicated logistics partner network is always ready to address any unexpected challenges, ensuring your goods reach their final destination intact and on time.
Transparent Tracking & Support
Visibility is key to smooth operations. We offer real-time tracking and regular updates so you’re always informed about the progress of your shipment. Our customer service team stands by to provide immediate support and answer any questions you might have. With detailed reporting at every step, you gain valuable insights that help optimize your supply chain operations for the future. With River Plate Inc. as your trusted logistics partner, you get more than just transportation. You get a freight logistics strategy built for efficiency, reliability, and growth.
With over 30 years of experience in logistics, we’ve mastered every aspect of freight logistics. Our industry knowledge ensures that each container is handled precisely through various transportation modes or intricate route planning. We’ve navigated challenges from fluctuating costs to complex delivery schedules, and our history shows that we adapt and excel.
Every business has unique shipping needs; no two freight projects are identical. Whether you require full container loads or a flexible partial shipment, our solutions are designed to scale with your growth. We work closely with you to tailor our services, optimizing transport to control cost without compromising delivery speed or reliability.
Our commitment to innovation means we continuously upgrade our systems. Advanced inventory management tools and real-time tracking technologies give you unmatched visibility into your cargo’s journey. By integrating thoughtful route planning and digital monitoring, we reduce errors, streamline operations, and ensure your freight is delivered on time, every time.
We understand that logistics can be complex and sometimes unpredictable. That’s why our dedicated customer service team is always on hand, offering expert advice and swift solutions. Whether you’re dealing with unexpected transport delays or planning a challenging multi-modal shipment, our team ensures a seamless process from start to finish.
Whether you’re scaling a growing Amazon FBA program or exploring Amazon FBM as an alternative, we adapt to fit your changing needs. Flexibility ensures your operations remain smooth, no matter how fast you grow.
We’re more than a logistics provider—we’re your partner. From optimizing your supply chain to helping you leverage tools like Amazon advertising, we work to support your long-term success. Together, we’ll bring your vision to life.
We specialize in ecommerce fulfillment in Los Angeles, warehousing, freight logistics, and value-added services all maximally tailored to your needs. We ensure real-time inventory tracking and efficient order fulfillment by integrating cutting-edge technology, which also includes our comprehensive warehouse management system (WMS). Our dedicated Client Success Managers work closely with each client and offer personalized support and strategic insights to help your business thrive.
We are strategically located in Simi Valley, CA, which allows us to deliver fast, accurate, and cost-effective services. Clients often praise our reliability, attention to detail, and ability to adapt to evolving industry demands.
At River Plate Inc., we like to operate as an extension of your team. We are deeply committed to the process of enhancing your supply chain and delivering exceptional customer satisfaction. Let us handle the logistics while you focus on growing your business.










































“We have worked with Riverplate for over 5 years and could not ask for a better 3PL partner. They have helped us launch two successful brands across different categories and regularly go above and beyond expectations. What truly sets them apart from other 3PLs is their flexibility and attention to detail. Whenever things do not go accordingly to plan, they do whatever they can to help. Also, in the rare instances when something is their fault, they have always taken responsibility and made the situation right. Lastly, they are always looking towards implementing new strategies/processes to improve efficiencies and save their clients money. To summarize, I could not recommend them more.”
Paul Richards
Speed matters in ecommerce, and so does accuracy. At our fulfillment center, we process orders quickly while also ensuring every detail is correct. Whether it’s a single product or a bulk shipment, our order fulfillment process minimizes errors and helps you maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Stay in control with real-time inventory tracking. Our advanced warehouse management system updates you instantly, so you always know what’s in stock. This reduces overselling and avoids backorders, which also ensures smooth operations for your ecommerce business.
Faster delivery starts with well-placed warehouses. Our strategically located fulfillment centers cut down on shipping times and costs, which gives your customers quicker access to their purchases. This makes your ecommerce fulfillment services more competitive and efficient.
Whether you’re scaling up for a big sales season or managing steady growth, our flexible fulfillment services adapt to your needs. From startups to established ecommerce platforms, we provide solutions that grow with your business and save you time and resources.
Shipping can be one of the biggest expenses in ecommerce, but our optimized logistics network reduces fulfillment costs without sacrificing speed. We partner with top carriers, like FedEx and others, to ensure you get the best shipping options at competitive rates.
Our team is here to guide you through every step, which offers personalized customer service to ensure your success.
Whether you’re managing a small Amazon store or scaling your FBA program, our solutions grow with your business needs.
From accurate order fulfillment to fast shipment times, we help you maintain a seamless experience for your customers, which drives loyalty and repeat sales.
We partner with ecommerce businesses of all sizes, from startups to established brands, across various industries. Whether you sell apparel, electronics, or home goods, we have a fulfillment solution for you.
We can integrate with platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, and more, which ensures a seamless connection between your store and our fulfillment services.
Yes we do, and our returns management services streamline the process and ensure that returned products are inspected, restocked, or processed according to your preferences.
Our strategically located warehouses and partnerships with top carriers allow us to offer competitive shipping options with faster delivery times.
Yes we do, and our returns management services streamline the process and ensure that returned products are inspected, restocked, or processed according to your preferences.
We use a real-time warehouse management system (WMS) that updates inventory instantly. This reduces errors and keeps you informed about stock levels at all times.
Yes, our fulfillment solutions are fully scalable. Whether you’re launching a new product line or handling seasonal spikes, we’ll adapt to your needs.
Yes, we specialize in big, heavy, and bulky fulfillment and offer customized solutions for products that don’t fit standard shipping options.
We use advanced technology and a multi-step quality control process to ensure every order is picked, packed, and shipped accurately.
Yes, we support international fulfillment services which help you reach customers around the globe with cost-effective and reliable shipping options.
You’ll have a dedicated Client Success Manager to address your needs, resolve issues, and ensure smooth operations.
Yes, we provide kitting and assembly services to bundle products, create gift sets, or prepare subscription boxes tailored to your business needs.
With over 30 years of experience, cutting-edge technology, and a client-first approach, we provide reliable, scalable, and efficient ecommerce fulfillment services designed to grow with your business.